
How to remove oxidation from aluminum
The alumina film provides many beneficial properties but may also limit some of the properties of aluminum. To remove oxidation from aluminum, here are 5 methods you can try:
1. Vinegar and Water Solution
– Create a mixture of equal parts white vinegar and water.
– Dip a soft cloth or sponge into the solution.
– Gently scrub the oxidized areas of the aluminum.
– Rinse the aluminum thoroughly with water and dry it with a clean cloth.
2. Baking Soda Paste
– Mix baking soda with water to create a thick paste.
– Apply the paste to the oxidized areas of the aluminum.
– Use a soft cloth or sponge to rub the paste onto the surface, applying gentle pressure.
– Rinse the aluminum with water and dry it with a clean cloth.

3. Lemon Juice and Cream of Tartar
– Squeeze fresh lemon juice into a bowl.
– Add a small amount of cream of tartar to the lemon juice to form a paste.
– Apply the paste to the oxidized areas of the aluminum.
– Leave the paste on the aluminum for 10-15 minutes.
– Use a soft cloth or sponge to scrub the paste onto the surface.
– Rinse the aluminum with water and dry it with a clean cloth.
4. Aluminum Brightener Products
– There are commercially available aluminum brightener products specifically designed to remove oxidation from aluminum.
– Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer on the product label.
– Typically, you would apply the product to the oxidized areas, let it sit for a specified amount of time, and then rinse it off thoroughly.
5. Sanding or Polishing
– For more stubborn oxidation or pitting, sanding or polishing the aluminum surface can be effective.
– Start with a coarse-grit sandpaper to remove the oxidation, then progressively move to finer-grit sandpaper for a smoother finish.
– After sanding, use a polishing compound and a soft cloth to restore shine to the aluminum surface.

Remember to test any cleaning method on a small, inconspicuous area of the aluminum before applying it to the entire surface. This will help ensure that the method does not cause any damage or discoloration. Additionally, take appropriate safety precautions, such as wearing gloves and working in a well-ventilated area, when using cleaning products.
Differences of different cleaning methods
There are three methods to remove oxidation from aluminum: chemical, mechanical and electrochemical. Each method has a different scope of application, and we can choose different methods according to the thickness of the aluminum oxide and the degree we want to remove.
The first is the most efficient chemical method, which is divided into three categories according to the different reagents:
– Acid washing: Use acidic solutions (such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid or oxalic acid) to corrode and dissolve the aluminum oxide film. This method is fast and effective and is suitable for the removal of large areas. It can completely remove oxidation from aluminum films in a relatively short period of time. However, acid washing may contaminate the environment and requires careful handling to ensure safety.

– Alkaline Cleaning: An alkaline solution (e.g., sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide) is used to dissolve the aluminum oxide film. The alkaline cleaning method is relatively gentle and has a low environmental impact. It is also effective in removing oxidation from aluminum, but is slower than acid washing.
– High Pressure Electrolysis: Aluminum parts are used as anodes to remove oxidation from aluminum by high pressure electrolysis. This method is suitable for small areas and complex shaped parts. It can be performed at lower temperatures and has less impact on the aluminum substrate. However, high-voltage electrolysis requires specialized equipment and techniques and is relatively complex to operate.
Mechanical methods are the simplest and most direct way to remove oxidation from aluminum, mainly by scraping or grinding, using scrapers, sandpaper, grinding wheels or other mechanical tools to physically erase the aluminum oxide film. This method is suitable for small areas and localized removal. It does not require the use of chemicals and therefore has a low environmental impact. However, mechanical methods may cause scratches or damage to the aluminum surface and may be less suitable for complex shaped parts.
Electrochemical methods are used to remove oxidation from aluminum by anodic redox, in which an aluminum part is used as an anode by applying an electric current in an electrolyte. This method can be performed at lower temperatures and has less impact on the aluminum substrate. It removes oxidation from aluminum and improves the quality of the aluminum surface. However, the electrochemical method requires specialized equipment and techniques and is relatively complex to operate, making it the most demanding of the three methods.
Each method has its own scenarios and limitations. Selection of the appropriate method depends on the specific application requirements, the shape and size of the part, and the operating conditions. Before selecting and using any method for removing oxidation from aluminum, it is recommended to refer to the relevant safety practices and ensure that appropriate safeguards are in place to protect the operator and avoid harm to the environment.
Structure of aluminum oxide
Aluminum oxide has the chemical formula Al2O3, expressed as a compound of one aluminum ion and three oxygen ions. The crystal structure of alumina belongs to the hexagonal densest packing structure, which is also known as the fibrous zincite structure. In the hexagonal densest-packed tructure, the aluminum and oxygen ions are arranged in a close-packed manner to form a hexagonal layer structure. The arrangement of aluminum and oxygen ions gives alumina a high degree of crystallinity, hardness and melting point.
In addition to the crystalline structure, alumina can also exist in an amorphous state. Amorphous alumina is formed when the crystallization process is inhibited due to rapid cooling or other preparation methods. Amorphous alumina has an irregular structure and its physical and chemical properties may differ from those of the crystalline form.
Aluminum oxide is formed as a result of a chemical reaction between aluminum and oxygen. This reaction is known as the oxidation of aluminum. At room temperature, a very thin film of aluminum oxide forms on the surface of aluminum, which is produced by the reaction of aluminum with oxygen in the air. This alumina film is corrosion resistant and protects the aluminum from further oxidation by oxygen.
When aluminum and oxygen in contact at high temperatures, the oxidation reaction will be more intense. At high temperatures, aluminum reacts rapidly with oxygen to produce aluminum oxide. This reaction can be expressed in a chemical equation as:
4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
In this reaction, four aluminum atoms react with three oxygen molecules to form two aluminum oxide molecules.
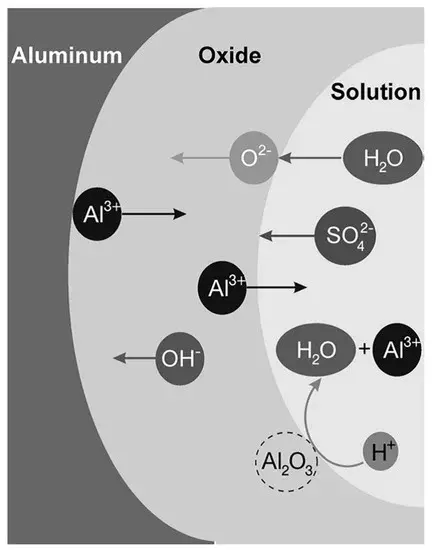
And, the production of aluminum oxide is an exothermic reaction that releases a lot of energy. This is one reason why bright sparks and flames appear when aluminum reacts with oxygen.
Anders als bei den meisten Reaktionen handelt es sich bei der Bildung von Aluminiumoxid um eine Oberflächenreaktion, die nur auf der Oberflächenschicht des Aluminiums abläuft. Sobald sich eine Aluminiumoxidschicht gebildet hat, wird die Reaktion automatisch gestoppt, da der Sauerstoff nicht in die dichte Aluminiumoxidschicht eindringen kann und dem Aluminium im Inneren der Schicht der notwendige Sauerstoff fehlt.
Hat die Bildung einer Oxidschicht Auswirkungen auf die Eigenschaften von Aluminium?
1. Erhöhte Korrosionsbeständigkeit: Die von Aluminiumoxid gebildete Aluminiumoxidschicht weist eine gute Korrosionsbeständigkeit auf und verhindert weitere Oxidationsreaktionen. Dies macht Aluminium sehr korrosionsbeständig und ermöglicht den Einsatz in einer Vielzahl von Umgebungsbedingungen, einschließlich nasser Umgebungen und saurer oder alkalischer Medien.
2. Erhöhte elektrische Isolierung: Die Aluminiumoxidschicht ist ein ausgezeichnetes elektrisches Isoliermaterial. Es hat hochisolierende Eigenschaften, die verhindern, dass Strom durch die Aluminiumoberfläche fließt. Dies macht Aluminiumoxid sehr nützlich für elektronische und elektrische Anwendungen wie Kondensatoren, integrierte Schaltkreise und Elektrolytkondensatoren.
3. Erhöhte Oberflächenhärte: Aluminiumoxidfolien sind härter als neue Aluminiumwerkstoffe. Dies verleiht Aluminiumoxid eine höhere Oberflächenhärte, die zusätzliche Widerstandsfähigkeit gegen Abrieb und Kratzer bietet. Infolgedessen kann Aluminiumoxid in einigen Anwendungen als Beschichtungsmaterial verwendet werden, das einen besseren Oberflächenschutz und eine längere Lebensdauer bietet.
4. Erhöhter Schmelzpunkt: Tonerde hat einen relativ hohen Schmelzpunkt von etwa 2072 Grad Celsius. Dadurch ist Aluminiumoxid sehr widerstandsfähig gegenüber hohen Temperaturen und in der Lage, seine strukturelle Stabilität in Hochtemperaturumgebungen aufrechtzuerhalten. Aus diesem Grund wird Aluminiumoxid häufig in Hochtemperaturanwendungen wie Hochtemperaturöfen, in der Keramikindustrie und in der Luft- und Raumfahrt eingesetzt.
Insgesamt wirkt sich die Bildung von Aluminiumoxid positiv auf die Eigenschaften und Verwendungszwecke von Aluminium aus, indem es seine Korrosionsbeständigkeit, elektrische Isolierung, Oberflächenhärte und Hochtemperaturbeständigkeit erhöht. Dies hat zu einer breiten Palette von Anwendungen für Aluminium und seine Aluminiumoxidschichten in vielen verschiedenen Bereichen geführt.

Wann entfernt man Oxidation von Aluminium?
Obwohl sich die Aluminiumoxidschicht in der Regel positiv auf die Eigenschaften und Verwendungsmöglichkeiten von Aluminium auswirkt, gibt es bestimmte Situationen, in denen es notwendig ist, die Oxidation von Aluminium zu entfernen.
1. Elektronische Komponenten: Aufgrund der Beschaffenheit von Aluminium selbst, das ein hoch leitfähiges Metall ist, finden wir Aluminium häufig in elektronischen Bauteilen. In den meisten dieser Anwendungen ist es jedoch erforderlich, dass Aluminium eine gute elektrische Leitfähigkeit beibehält, und die Aluminiumoxidschicht ist ein isolierendes Material, das die Leitfähigkeit von Aluminium verringert. Daher müssen wir in diesem Fall die Oxidation von Aluminium entfernen, um die Leitfähigkeit von Aluminium wiederherzustellen.
2. Schweißen und Fügen: Die Aluminiumoxidschicht ist ein Hindernis für die Metallverbindung beim Schweißen und Fügen, da sie einen engen Kontakt und die Diffusion zwischen den Metallen verhindert. Um ein gutes Schweißen oder Kleben zu gewährleisten, müssen wir in diesem Fall auch die Oxidation von Aluminium entfernen.

3. Oberflächenbehandlung: Bei einigen Anwendungen ist eine weitere Behandlung der Aluminiumoberfläche erforderlich, z. B. durch Beschichtung, Lackierung oder Verklebung. Die Aluminiumoxidschicht kann die Qualität und Haftung dieser Behandlungen beeinträchtigen. Entfernen Sie daher die Oxidation von Aluminium, um eine bessere Oberfläche zu erhalten.
4. Anti-Korrosions-Behandlung: Obwohl die Aluminium-Oxid-Film selbst hat ein gewisses Maß an Korrosionsbeständigkeit, aber in einigen speziellen Umgebungen, kann es notwendig sein, strengere Anti-Korrosions-Behandlung von Aluminium, die auch müssen zunächst entfernen Oxidation von Aluminium-Oberfläche, die durch die Oxid-Film, so dass andere korrosionsbeständige Materialien können besser haften zu führen.
In diesen Fällen können wir die oben erwähnte Methode zur Entfernung von Aluminiumoxid anwenden, um das Problem zu lösen. In der Praxis können wir chemische, mechanische oder elektrochemische Methoden anwenden, um Oxidation von Aluminium zu entfernen, je nach der tatsächlichen Situation. Es ist zu beachten, dass nach der Entfernung der Oxidation von Aluminium geeignete Maßnahmen zum Schutz der Aluminiumoberfläche getroffen werden müssen, um eine erneute Oxidation und Korrosion zu verhindern. Dies kann durch eine Oberflächenbeschichtung oder durch Isolierung der Umgebung von Sauerstoff erreicht werden.
Ist Aluminium eine Legierung? Oxidationsbeständigkeit von verschiedenen Aluminiumlegierungen.
Legierungen werden durch die Kombination eines unedlen Metalls mit einem oder mehreren anderen Elementen gebildet. Aluminium selbst ist ein chemisches Element mit dem Symbol Al und der Ordnungszahl 13 und keine Legierung. Es ist ein leichtes und verformbares Metall.
Aluminium wird jedoch häufig mit anderen Elementen legiert, um seine Eigenschaften für bestimmte Anwendungen zu verbessern, z. B. mit Kupfer, Magnesium, Silizium, Zink usw. Diese Legierungselemente werden hinzugefügt, um die Eigenschaften von Aluminium zu verändern, wie z. B. Festigkeit, Härte, Korrosionsbeständigkeit und Hitzebeständigkeit. Die verschiedenen Aluminiumlegierungen weisen unterschiedliche Oxidationsbeständigkeiten auf, die von den der Legierung zugesetzten Legierungselementen und der Legierungsbehandlung abhängen. Im Folgenden finden Sie Beispiele für einige gängige Aluminiumlegierungen und ihr Grad an Oxidationsbeständigkeit
| Legierungsgruppe | Wichtiges Legierungselement | Stärke | Duktilität | Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Schweißeignung | Eloxieren |
| Baureihe 1xxx | Keine | Niedrig | Hoch | Hoch | Hoch | Hoch+ |
| Baureihe 2xxx | Cu | Hoch+ | Niedrig | Niedrig | Niedrig | Niedrig |
| Baureihe 3xxx | Mn | Niedrig+ | Hoch | Hoch | Hoch | Hoch |
| Baureihe 5xxx | Mg | Mitte | Mitte | Hoch | Hoch | Hoch |
| Baureihe 6xxx | Si/Mg | Mitte | Mitte | Hoch | Hoch | Hoch+ |
| Baureihe 7xxx | Zn/Mg | Hoch | Niedrig | Mitte | Mitte | Mitte |
Welche Legierung hat die stärkste Oxidationsbeständigkeit?
Die Aluminiumlegierungsserie 7xxx (Aluminium-Zink-Legierung) gilt als diejenige mit der höchsten Oxidationsbeständigkeit. Dies ist auf den Zusatz von Zink zu der Aluminium-Zink-Legierung zurückzuführen, die eine hohe Korrosions- und Oxidationsbeständigkeit aufweist. Der Zinkzusatz fördert die Bildung und Verdickung des Aluminiumoxidfilms und bildet eine dichte Schutzschicht, die wirksam verhindert, dass Sauerstoff und andere schädliche Stoffe die Aluminiumlegierung weiter angreifen.


