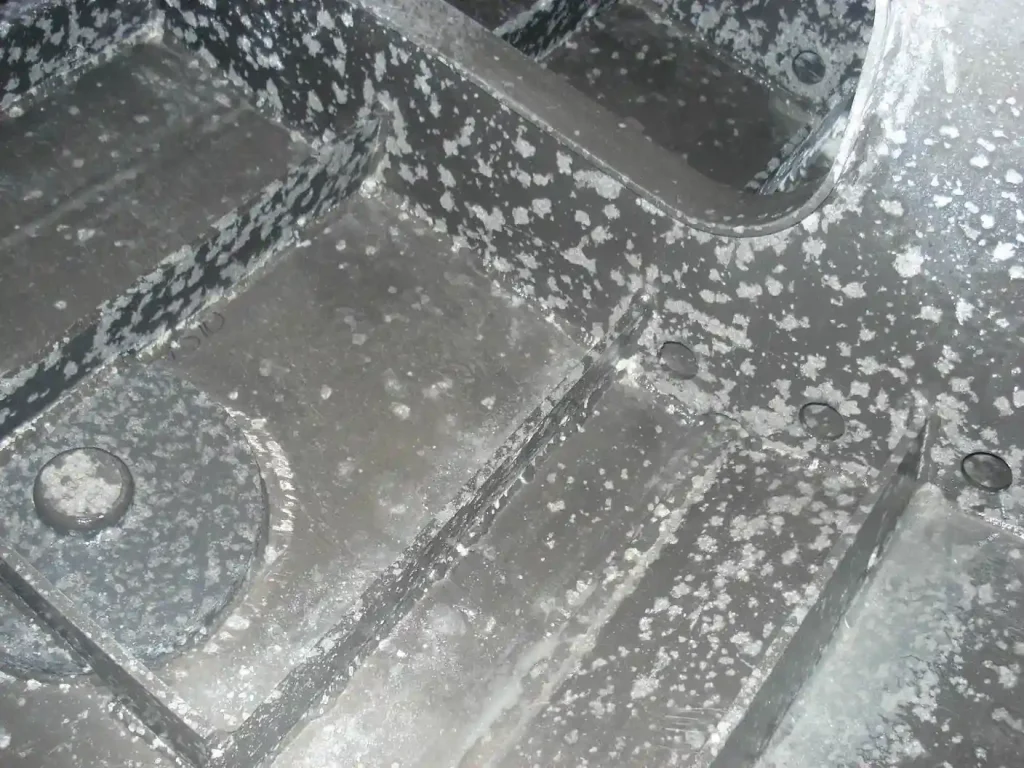

Comment enlever l'oxydation de l'aluminium
Le film d'alumine offre de nombreuses propriétés bénéfiques, mais peut également limiter certaines des propriétés de l'aluminium. Pour éliminer l'oxydation de l'aluminium, voici 5 méthodes que vous pouvez essayer :
1. Solution de vinaigre et d'eau
- Créez un mélange à parts égales de vinaigre blanc et d'eau.
- Tremper un chiffon doux ou une éponge dans la solution.
- Frottez doucement les zones oxydées de l'aluminium.
- Rincez soigneusement l'aluminium à l'eau et séchez-le avec un chiffon propre.
2. Pâte de bicarbonate de soude
- Mélangez du bicarbonate de soude avec de l'eau pour obtenir une pâte épaisse.
- Appliquer la pâte sur les zones oxydées de l'aluminium.
- Utilisez un chiffon doux ou une éponge pour frotter la pâte sur la surface, en exerçant une légère pression.
- Rincez l'aluminium à l'eau et séchez-le avec un chiffon propre.

3. Jus de citron et crème de tartre
- Presser le jus de citron frais dans un bol.
- Ajouter une petite quantité de crème de tartre au jus de citron pour former une pâte.
- Appliquer la pâte sur les zones oxydées de l'aluminium.
- Laisser la pâte sur l'aluminium pendant 10 à 15 minutes.
- Utilisez un chiffon doux ou une éponge pour frotter la pâte sur la surface.
- Rincez l'aluminium à l'eau et séchez-le avec un chiffon propre.
4. Produits de blanchiment de l'aluminium
- Il existe dans le commerce des produits de blanchiment de l'aluminium spécialement conçus pour éliminer l'oxydation de l'aluminium.
- Suivez les instructions fournies par le fabricant sur l'étiquette du produit.
- En règle générale, vous appliquez le produit sur les zones oxydées, vous le laissez agir pendant une durée déterminée, puis vous le rincez abondamment.
5. Ponçage ou polissage
- En cas d'oxydation ou de piqûres plus tenaces, le ponçage ou le polissage de la surface de l'aluminium peut s'avérer efficace.
- Commencez par un papier de verre à gros grain pour éliminer l'oxydation, puis passez progressivement à un papier de verre à grain plus fin pour obtenir une finition plus lisse.
- Après le ponçage, utilisez un produit de polissage et un chiffon doux pour redonner de l'éclat à la surface de l'aluminium.

N'oubliez pas de tester toute méthode de nettoyage sur une petite zone peu visible de l'aluminium avant de l'appliquer à l'ensemble de la surface. Cela permet de s'assurer que la méthode ne cause pas de dommages ou de décoloration. En outre, prenez les mesures de sécurité qui s'imposent, comme le port de gants et le travail dans un endroit bien ventilé, lorsque vous utilisez des produits de nettoyage.
Différences entre les différentes méthodes de nettoyage
Il y a trois méthodes pour éliminer l'oxydation de l'aluminiumLes méthodes d'élimination de l'oxyde d'aluminium sont les suivantes : chimique, mécanique et électrochimique. Chaque méthode a un champ d'application différent, et nous pouvons choisir différentes méthodes en fonction de l'épaisseur de l'oxyde d'aluminium et du degré que nous voulons éliminer.
La première est la méthode chimique la plus efficace, qui se divise en trois catégories en fonction des différents réactifs :
- Lavage à l'acide : utiliser des solutions acides (telles que l'acide sulfurique, l'acide chlorhydrique ou l'acide oxalique) pour corroder et dissoudre le film d'oxyde d'aluminium. Cette méthode est rapide et efficace et convient à l'élimination de grandes surfaces. Elle permet d'éliminer complètement l'oxydation des films d'aluminium en un temps relativement court. Toutefois, le lavage à l'acide peut contaminer l'environnement et doit être manipulé avec précaution pour garantir la sécurité.

- Nettoyage alcalin : Une solution alcaline (par exemple, de l'hydroxyde de sodium ou de potassium) est utilisée pour dissoudre le film d'oxyde d'aluminium. La méthode de nettoyage alcalin est relativement douce et a un faible impact sur l'environnement. Elle est également efficace pour éliminer l'oxydation de l'aluminium, mais elle est plus lente que le lavage à l'acide.
- Électrolyse à haute pression : Les pièces en aluminium sont utilisées comme anodes pour éliminer l'oxydation de l'aluminium par électrolyse à haute pression. Cette méthode convient aux petites surfaces et aux pièces de forme complexe. Elle peut être réalisée à des températures plus basses et a moins d'impact sur le substrat d'aluminium. Cependant, l'électrolyse à haute tension nécessite un équipement et des techniques spécialisés et est relativement complexe à mettre en œuvre.
Les méthodes mécaniques constituent le moyen le plus simple et le plus direct d'éliminer l'oxydation de l'aluminium, principalement par grattage ou meulage, en utilisant des grattoirs, du papier de verre, des meules ou d'autres outils mécaniques pour effacer physiquement le film d'oxyde d'aluminium. Cette méthode convient aux petites surfaces et à l'élimination localisée. Elle ne nécessite pas l'utilisation de produits chimiques et a donc un faible impact sur l'environnement. Toutefois, les méthodes mécaniques peuvent causer des rayures ou des dommages à la surface de l'aluminium et peuvent être moins adaptées aux pièces de forme complexe.
Les méthodes électrochimiques sont utilisées pour éliminer l'oxydation de l'aluminium par oxydoréduction anodique, dans laquelle une pièce d'aluminium est utilisée comme anode en appliquant un courant électrique dans un électrolyte. Cette méthode peut être appliquée à des températures plus basses et a moins d'impact sur le substrat d'aluminium. Elle élimine l'oxydation de l'aluminium et améliore la qualité de la surface de l'aluminium. Cependant, la méthode électrochimique nécessite un équipement et des techniques spécialisés et est relativement complexe à mettre en œuvre, ce qui en fait la méthode la plus exigeante des trois.
Chaque méthode a ses propres scénarios et limites. Le choix de la méthode appropriée dépend des exigences spécifiques de l'application, de la forme et de la taille de la pièce et des conditions d'utilisation. Avant de choisir et d'utiliser une méthode pour éliminer l'oxydation de l'aluminium, il est recommandé de se référer aux pratiques de sécurité pertinentes et de s'assurer que les mesures de protection appropriées sont en place pour protéger l'opérateur et éviter de nuire à l'environnement.
Structure de l'oxyde d'aluminium
La formule chimique de l'oxyde d'aluminium est la suivante Al2O3L'alumine est un composé d'un ion d'aluminium et de trois ions d'oxygène. La structure cristalline de l'alumine appartient à la structure hexagonale la plus dense, également connue sous le nom de structure de zincite fibreuse. Dans la structure hexagonale la plus dense, les ions d'aluminium et d'oxygène sont disposés en couches serrées pour former une structure hexagonale. La disposition des ions d'aluminium et d'oxygène confère à l'alumine un degré élevé de cristallinité, de dureté et de point de fusion.
Outre la structure cristalline, l'alumine peut également exister à l'état amorphe. L'alumine amorphe se forme lorsque le processus de cristallisation est inhibé par un refroidissement rapide ou d'autres méthodes de préparation. L'alumine amorphe a une structure irrégulière et ses propriétés physiques et chimiques peuvent différer de celles de la forme cristalline.
L'oxyde d'aluminium est le résultat d'une réaction chimique entre l'aluminium et l'oxygène. Cette réaction est connue sous le nom d'oxydation de l'aluminium. À température ambiante, une très fine pellicule d'oxyde d'aluminium se forme à la surface de l'aluminium, par réaction de l'aluminium avec l'oxygène de l'air. Cette pellicule d'alumine résiste à la corrosion et protège l'aluminium d'une nouvelle oxydation par l'oxygène.
Lorsque l'aluminium et l'oxygène sont en contact à des températures élevées, la réaction d'oxydation est plus intense. À haute température, l'aluminium réagit rapidement avec l'oxygène pour produire de l'oxyde d'aluminium. Cette réaction peut être exprimée dans une équation chimique comme suit :
4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
Dans cette réaction, quatre atomes d'aluminium réagissent avec trois molécules d'oxygène pour former deux molécules d'oxyde d'aluminium.
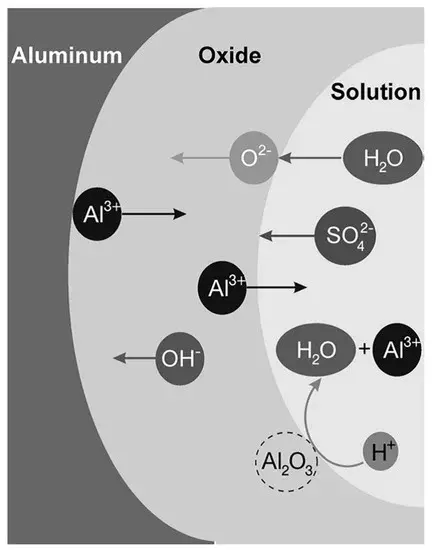
And, the production of aluminum oxide is an exothermic reaction that releases a lot of energy. This is one reason why bright sparks and flames appear when aluminum reacts with oxygen.
Unlike most reactions, the formation of alumina is a surface reaction, occurring only on the surface layer of aluminum. Once an alumina film is formed, the reaction will automatically stop because oxygen cannot penetrate the dense alumina film and the aluminum inside the film lacks the necessary oxygen.
Does the formation of an oxide film have any effect on the properties of aluminum?
1. Enhanced corrosion resistance: The alumina film formed by alumina has good corrosion resistance and prevents further oxidation reactions from occurring. This makes aluminum highly resistant to corrosion and allows it to be used in a variety of environmental conditions, including wet environments and acidic or alkaline media.
2. Increased electrical insulation: Aluminum oxide film is an excellent electrical insulating material. It has high insulating properties that prevent current from flowing through the aluminum surface. This makes aluminum oxide very useful in electronic and electrical applications such as capacitors, integrated circuits and electrolytic capacitors.
3. Increased surface hardness: Alumina films are harder than virgin aluminum materials. This gives alumina a higher surface hardness that provides additional resistance to abrasion and scratching. As a result, aluminum oxide can be used as a coating material in some applications, providing better surface protection and durability.
4. Increased melting point: Alumina has a relatively high melting point of approximately 2072 degrees Celsius. This makes alumina highly resistant to high temperatures and able to maintain structural stability in high temperature environments. As a result, alumina is widely used in high-temperature applications, such as high-temperature furnaces, the ceramics industry and aerospace.
Overall, the formation of alumina positively affects the properties and uses of aluminum by increasing its corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, surface hardness, and high temperature resistance. This has led to a wide range of applications for aluminum and its alumina films in many different fields.

When do we remove oxidation from aluminum?
Although the aluminum oxide film usually has a positive effect on the properties and uses of aluminum, there are certain situations in which it is necessary to remove oxidation from aluminum.
1. Electronic components: Because of the nature of aluminum itself, which is a highly conductive metal, we often find aluminum in electronic components. However, in most of these applications, aluminum is required to maintain good electrical conductivity, and aluminum oxide film is an insulating material that reduces the conductivity of aluminum. Therefore, in this case, we need to remove oxidation from aluminum to restore the conductivity of aluminum.
2. Welding and Joining: Aluminum oxide film is an obstacle to metal connection during welding and joining because it prevents close contact and diffusion between metals. In order to ensure good welding or bonding, in this case we also need to remove oxidation from aluminum.

3. Surface treatment: In some applications, further treatment of the aluminum surface is required, such as coating, painting or bonding. Aluminum oxide film may affect the quality and adhesion of these treatments. Therefore, remove oxidation from aluminum to obtain a better surface finish.
4. Anti-corrosion treatment: Although the aluminum oxide film itself has a certain degree of corrosion resistance, but in some special environments, it may be necessary to carry out more stringent anti-corrosion treatment of aluminum, which also need to first remove oxidation from aluminum surface generated by the oxide film, so that other corrosion-resistant materials can be better adhered to.
In these cases, we can apply the above mentioned method of removing aluminum oxide to deal with it. In practice, we can use chemical, mechanical or electrochemical methods to remove oxidation from aluminum, depending on the actual situation. It should be noted that after we remove oxidation from aluminum, we need to take appropriate measures to protect the aluminum surface to prevent re-oxidation and corrosion. This can be achieved by surface coating or by isolating the environment from oxygen.
Is aluminum an alloy? Oxidation resistance of different aluminum alloys.
Alloys are formed by combining a base metal with one or more other elements. Aluminum itself is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13 not an alloy. It is a lightweight and malleable metal.
However, aluminum is often alloyed with other elements to enhance its properties for specific applications, such as copper, magnesium, silicon, zinc, etc. These alloying elements are added to alter the properties of aluminum, such as strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance. Different aluminum alloys have different degrees of oxidation resistance, which is determined by the alloying elements added to the alloy and the alloying treatment. Below are examples of several common aluminum alloys and their degree of oxidation resistance
| Alloy Group | Major Alloying Element | La force | Ductility | Résistance à la corrosion | Soudabilité | Anodisation |
| 1xxx series | None | Faible | Haut | Haut | Haut | High+ |
| 2xxx series | Cu | High+ | Faible | Faible | Faible | Faible |
| 3xxx series | Mn | Low+ | Haut | Haut | Haut | Haut |
| 5xxx series | Mg | Middle | Middle | Haut | Haut | Haut |
| Série 6xxx | Si/Mg | Middle | Middle | Haut | Haut | High+ |
| 7xxx series | Zn/Mg | Haut | Faible | Middle | Middle | Middle |
Which alloy have the strongest oxidation resistance?
The aluminum alloy series 7xxx (aluminum-zinc alloy) is considered to have the strongest oxidation resistance. This is due to the addition of zinc to the aluminum-zinc alloy, which has high corrosion and oxidation resistance. The addition of zinc promotes the formation and thickening of the alumina film, forming a dense protective layer that effectively prevents oxygen and other harmful substances from further attacking the aluminum alloy.


