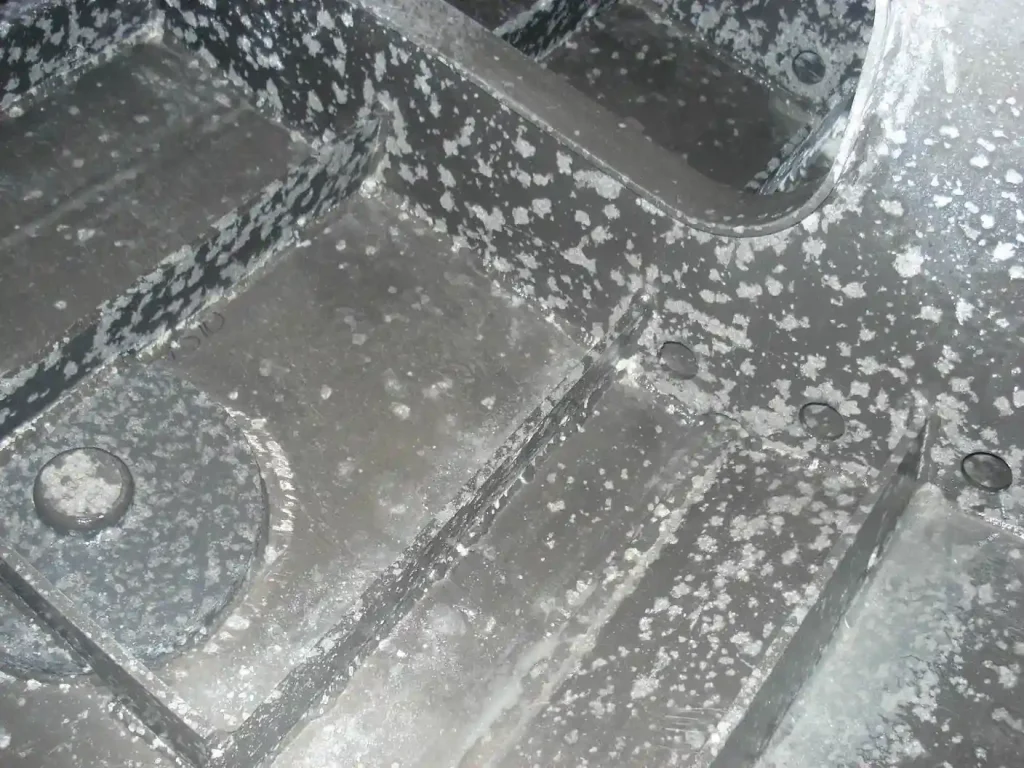

How to remove oxidation from aluminum
The alumina film provides many beneficial properties but may also limit some of the properties of aluminum. To remove oxidation from aluminum, here are 5 methods you can try:
1. Vinegar and Water Solution
– Create a mixture of equal parts white vinegar and water.
– Dip a soft cloth or sponge into the solution.
– Gently scrub the oxidized areas of the aluminum.
– Rinse the aluminum thoroughly with water and dry it with a clean cloth.
2. Baking Soda Paste
– Mix baking soda with water to create a thick paste.
– Apply the paste to the oxidized areas of the aluminum.
– Use a soft cloth or sponge to rub the paste onto the surface, applying gentle pressure.
– Rinse the aluminum with water and dry it with a clean cloth.
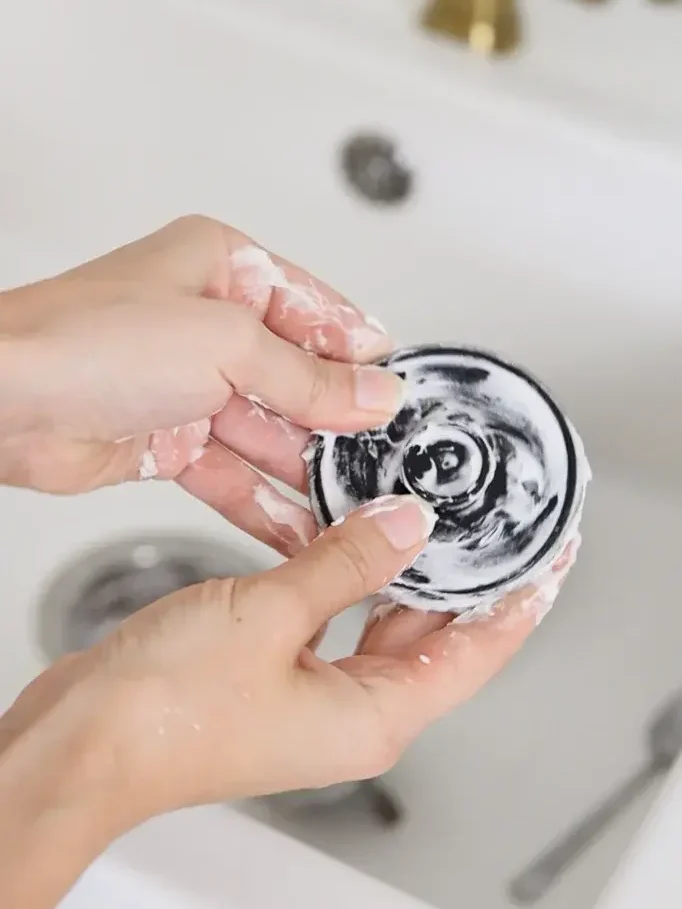

3. Lemon Juice and Cream of Tartar
– Squeeze fresh lemon juice into a bowl.
– Add a small amount of cream of tartar to the lemon juice to form a paste.
– Apply the paste to the oxidized areas of the aluminum.
– Leave the paste on the aluminum for 10-15 minutes.
– Use a soft cloth or sponge to scrub the paste onto the surface.
– Rinse the aluminum with water and dry it with a clean cloth.
4. Aluminum Brightener Products
– There are commercially available aluminum brightener products specifically designed to remove oxidation from aluminum.
– Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer on the product label.
– Typically, you would apply the product to the oxidized areas, let it sit for a specified amount of time, and then rinse it off thoroughly.
5. Sanding or Polishing
– For more stubborn oxidation or pitting, sanding or polishing the aluminum surface can be effective.
– Start with a coarse-grit sandpaper to remove the oxidation, then progressively move to finer-grit sandpaper for a smoother finish.
– After sanding, use a polishing compound and a soft cloth to restore shine to the aluminum surface.

Remember to test any cleaning method on a small, inconspicuous area of the aluminum before applying it to the entire surface. This will help ensure that the method does not cause any damage or discoloration. Additionally, take appropriate safety precautions, such as wearing gloves and working in a well-ventilated area, when using cleaning products.
Differences of different cleaning methods
There are three methods to remove oxidation from aluminum: chemical, mechanical and electrochemical. Each method has a different scope of application, and we can choose different methods according to the thickness of the aluminum oxide and the degree we want to remove.
The first is the most efficient chemical method, which is divided into three categories according to the different reagents:
– Acid washing: Use acidic solutions (such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid or oxalic acid) to corrode and dissolve the aluminum oxide film. This method is fast and effective and is suitable for the removal of large areas. It can completely remove oxidation from aluminum films in a relatively short period of time. However, acid washing may contaminate the environment and requires careful handling to ensure safety.

– Alkaline Cleaning: An alkaline solution (e.g., sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide) is used to dissolve the aluminum oxide film. The alkaline cleaning method is relatively gentle and has a low environmental impact. It is also effective in removing oxidation from aluminum, but is slower than acid washing.
– High Pressure Electrolysis: Aluminum parts are used as anodes to remove oxidation from aluminum by high pressure electrolysis. This method is suitable for small areas and complex shaped parts. It can be performed at lower temperatures and has less impact on the aluminum substrate. However, high-voltage electrolysis requires specialized equipment and techniques and is relatively complex to operate.
Mechanical methods are the simplest and most direct way to remove oxidation from aluminum, mainly by scraping or grinding, using scrapers, sandpaper, grinding wheels or other mechanical tools to physically erase the aluminum oxide film. This method is suitable for small areas and localized removal. It does not require the use of chemicals and therefore has a low environmental impact. However, mechanical methods may cause scratches or damage to the aluminum surface and may be less suitable for complex shaped parts.
Electrochemical methods are used to remove oxidation from aluminum by anodic redox, in which an aluminum part is used as an anode by applying an electric current in an electrolyte. This method can be performed at lower temperatures and has less impact on the aluminum substrate. It removes oxidation from aluminum and improves the quality of the aluminum surface. However, the electrochemical method requires specialized equipment and techniques and is relatively complex to operate, making it the most demanding of the three methods.
Each method has its own scenarios and limitations. Selection of the appropriate method depends on the specific application requirements, the shape and size of the part, and the operating conditions. Before selecting and using any method for removing oxidation from aluminum, it is recommended to refer to the relevant safety practices and ensure that appropriate safeguards are in place to protect the operator and avoid harm to the environment.
Structure of aluminum oxide
Aluminum oxide has the chemical formula Al2O3, expressed as a compound of one aluminum ion and three oxygen ions. The crystal structure of alumina belongs to the hexagonal densest packing structure, which is also known as the fibrous zincite structure. In the hexagonal densest-packed tructure, the aluminum and oxygen ions are arranged in a close-packed manner to form a hexagonal layer structure. The arrangement of aluminum and oxygen ions gives alumina a high degree of crystallinity, hardness and melting point.
In addition to the crystalline structure, alumina can also exist in an amorphous state. Amorphous alumina is formed when the crystallization process is inhibited due to rapid cooling or other preparation methods. Amorphous alumina has an irregular structure and its physical and chemical properties may differ from those of the crystalline form.
Aluminum oxide is formed as a result of a chemical reaction between aluminum and oxygen. This reaction is known as the oxidation of aluminum. At room temperature, a very thin film of aluminum oxide forms on the surface of aluminum, which is produced by the reaction of aluminum with oxygen in the air. This alumina film is corrosion resistant and protects the aluminum from further oxidation by oxygen.
When aluminum and oxygen in contact at high temperatures, the oxidation reaction will be more intense. At high temperatures, aluminum reacts rapidly with oxygen to produce aluminum oxide. This reaction can be expressed in a chemical equation as:
4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
In this reaction, four aluminum atoms react with three oxygen molecules to form two aluminum oxide molecules.
And, the production of aluminum oxide is an exothermic reaction that releases a lot of energy. This is one reason why bright sparks and flames appear when aluminum reacts with oxygen.
Unlike most reactions, the formation of alumina is a surface reaction, occurring only on the surface layer of aluminum. Once an alumina film is formed, the reaction will automatically stop because oxygen cannot penetrate the dense alumina film and the aluminum inside the film lacks the necessary oxygen.
Does the formation of an oxide film have any effect on the properties of aluminum?
1. Enhanced corrosion resistance: The alumina film formed by alumina has good corrosion resistance and prevents further oxidation reactions from occurring. This makes aluminum highly resistant to corrosion and allows it to be used in a variety of environmental conditions, including wet environments and acidic or alkaline media.
2. Increased electrical insulation: Aluminum oxide film is an excellent electrical insulating material. It has high insulating properties that prevent current from flowing through the aluminum surface. This makes aluminum oxide very useful in electronic and electrical applications such as capacitors, integrated circuits and electrolytic capacitors.
3. Increased surface hardness: Alumina films are harder than virgin aluminum materials. This gives alumina a higher surface hardness that provides additional resistance to abrasion and scratching. As a result, aluminum oxide can be used as a coating material in some applications, providing better surface protection and durability.
4. Increased melting point: Alumina has a relatively high melting point of approximately 2072 degrees Celsius. This makes alumina highly resistant to high temperatures and able to maintain structural stability in high temperature environments. As a result, alumina is widely used in high-temperature applications, such as high-temperature furnaces, the ceramics industry and aerospace.
Overall, the formation of alumina positively affects the properties and uses of aluminum by increasing its corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, surface hardness, and high temperature resistance. This has led to a wide range of applications for aluminum and its alumina films in many different fields.

When do we remove oxidation from aluminum?
Although the aluminum oxide film usually has a positive effect on the properties and uses of aluminum, there are certain situations in which it is necessary to remove oxidation from aluminum.
1. Electronic components: Because of the nature of aluminum itself, which is a highly conductive metal, we often find aluminum in electronic components. However, in most of these applications, aluminum is required to maintain good electrical conductivity, and aluminum oxide film is an insulating material that reduces the conductivity of aluminum. Therefore, in this case, we need to remove oxidation from aluminum to restore the conductivity of aluminum.
2. Welding and Joining: Aluminum oxide film is an obstacle to metal connection during welding and joining because it prevents close contact and diffusion between metals. In order to ensure good welding or bonding, in this case we also need to remove oxidation from aluminum.

3. Surface treatment: In some applications, further treatment of the aluminum surface is required, such as coating, painting or bonding. Aluminum oxide film may affect the quality and adhesion of these treatments. Therefore, remove oxidation from aluminum to obtain a better surface finish.
4. Anti-corrosion treatment: Although the aluminum oxide film itself has a certain degree of corrosion resistance, but in some special environments, it may be necessary to carry out more stringent anti-corrosion treatment of aluminum, which also need to first remove oxidation from aluminum surface generated by the oxide film, so that other corrosion-resistant materials can be better adhered to.
In these cases, we can apply the above mentioned method of removing aluminum oxide to deal with it. In practice, we can use chemical, mechanical or electrochemical methods to remove oxidation from aluminum, depending on the actual situation. It should be noted that after we remove oxidation from aluminum, we need to take appropriate measures to protect the aluminum surface to prevent re-oxidation and corrosion. This can be achieved by surface coating or by isolating the environment from oxygen.
Is aluminum an alloy? Oxidation resistance of different aluminum alloys.
Alloys are formed by combining a base metal with one or more other elements. Aluminum itself is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13 not an alloy. It is a lightweight and malleable metal.
However, aluminum is often alloyed with other elements to enhance its properties for specific applications, such as copper, magnesium, silicon, zinc, etc. These alloying elements are added to alter the properties of aluminum, such as strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance. Different aluminum alloys have different degrees of oxidation resistance, which is determined by the alloying elements added to the alloy and the alloying treatment. Below are examples of several common aluminum alloys and their degree of oxidation resistance
| Alloy Group | Major Alloying Element | Strength | Ductility | Corrosion Resistance | Weldability | Anodizing |
| 1xxx series | None | Low | High | High | High | High+ |
| 2xxx series | Cu | High+ | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| 3xxx series | Mn | Low+ | High | High | High | High |
| 5xxx series | Mg | Middle | Middle | High | High | High |
| 6xxx series | Si/Mg | Middle | Middle | High | High | High+ |
| 7xxx series | Zn/Mg | High | Low | Middle | Middle | Middle |
Which alloy have the strongest oxidation resistance?
The aluminum alloy series 7xxx (aluminum-zinc alloy) is considered to have the strongest oxidation resistance. This is due to the addition of zinc to the aluminum-zinc alloy, which has high corrosion and oxidation resistance. The addition of zinc promotes the formation and thickening of the alumina film, forming a dense protective layer that effectively prevents oxygen and other harmful substances from further attacking the aluminum alloy.


