In the quest for energy-efficient cooling systems that meet stringent environmental standards, hydrophilic aluminum foil has emerged as a game-changer in modern HVAC innovation. As global demand surges for air conditioners that balance peak thermal performance with sustainability, this engineered foil—coated with a microscopically porous hydrophilic layer—is redefining evaporator and condenser coil efficiency.
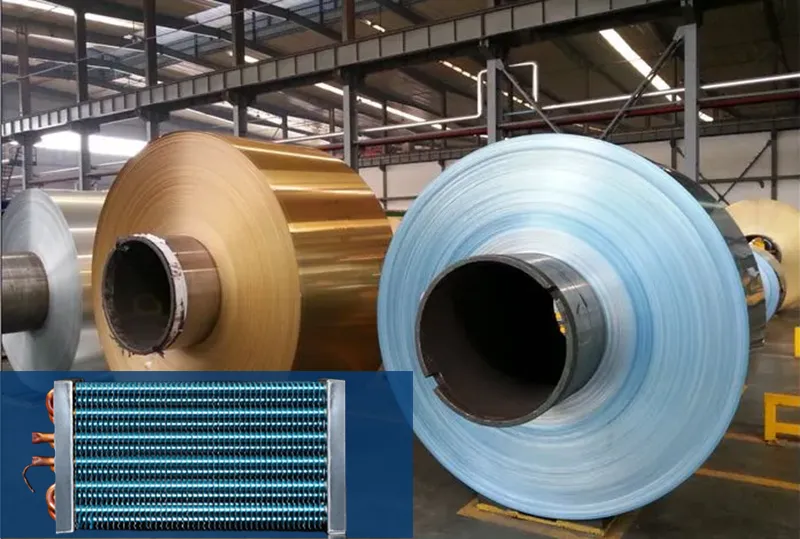

Leading manufacturers now prioritize hydrophilic aluminum foil for air conditioners not only for its 30% higher heat transfer rates compared to conventional foils but also for its anti-corrosion properties that extend equipment lifespan in humid climates. This article explores how advanced hydrophilic coatings combat frost formation, reduce energy consumption by up to 15%, and align with EPA refrigerant transition protocols, positioning this material as the cornerstone of next-gen HVAC design.
What Is Hydrophilic Foil
Compared with ordinary aluminum foil, hydrophilic foil has a hydrophilic coating and an anti-corrosion coating on the surface. Hydrophilic aluminum foil is mainly used for air conditioner radiator fins.
The principle of using hydrophilic foil in the air conditioning industry is that the condensed water in the air conditioner will quickly spread on the hydrophilic foil and will not condense into water droplets, thereby increasing the heat exchange area, speeding up the cooling and heating speed, and effectively avoiding noise.
Hydrophilic aluminum foil is a type of air-conditioning foil, but it cannot be completely regarded as air-conditioning foil. In addition to hydrophilic foil, non-coated aluminum foil, corrosion-resistant aluminum foil, hydrophobic aluminum foil, lubricating aluminum foil, etc. are also air-conditioning foils.
Aluminum Hydrophilic Foil Alloy
Hydrophilic aluminum foil is an important material widely used in refrigeration equipment such as household air conditioners, refrigerators, automobile air conditioners, and automobile water tanks.
| Series/Alloy | 1000 series: 1100, 1200 3000 series: 3003, 3102, 3015 8000 series: 8011, 8079 |
| Temper | O, H22, H24, H26, etc |
| Thickness | 0.08-0.2mm |
| Width | 1400mm, customized |
| Inner Diameter | 76/152/200mm |
| Key Properties | 1xxx series: 99%+ purity, superior corrosion resistance 3xxx series: Mn-enhanced strength, excellent deep-drawing 8xxx series: Fe/Si optimization, enhanced brazeability |
| HVAC Applications | 1000 series: Humid coastal environments 3000 series: High-pressure condenser coils 8000 series: Multi-layer brazed heat exchangers |
Industry-Standard Dimensions:
| Parameter | Range | Typical HVAC Use Case |
| Thickness | 0.08–0.2 mm | 0.1 mm for microchannel, 0.15 mm for tube-fin |
| Width | 300–1,300 mm | 950 mm (standard coil width for Carrier/Trane) |
| Coil Length | 2,000–8,000 m | Optimized for high-speed stamping (≥120 fins/min) |

Air conditioning hydrophilic foil mainly uses 3xxx and 8xxx series aluminum alloys, taking into account strength, formability, and corrosion resistance.
- 8011 alloy: contains Fe 0.5%-1.0%, Si 0.4%-0.8%, H18 state (tensile strength ≥160 MPa). The advantage lies in excellent brazing compatibility and is suitable for multi-layer composite heat exchangers. Its high Fe content can refine the grains and improve the dimensional stability of stamped fins (tolerance ±0.02 mm).
- 3102 alloy: contains Mn 0.05%-0.20%, Cu≤0.05%, and O temper (soft temper). It is known for its high elongation (≥25%) and is suitable for complex fin designs (such as louver type), but its corrosion resistance is slightly inferior to 8011 and needs to rely on coating protection.
Performance Comparison:
| Parameter | 8011 H18 | 3102 O |
| Tension Strength | 160-180 MPa | 80-100 MPa |
| Elongation | 2%-4% | 25%-30% |
| Applicable Process | Brazing/high frequency welding | Stamping/bending |
| Cost | Middle | Low |
Currently, the North American market prefers 3102 alloy for low-corrosion environments, while the Asian market mostly uses 8011 alloy to cope with high humidity challenges.
Hydrophilic Coating Technology And Detection
The core technologies of hydrophilic coatings include pretreatment, coating formulation, and curing processes.
1. Pretreatment:
- Degreasing: alkaline cleaning agent (pH 10-12) to remove rolling oil.
- Chemical conversion: chromium-free zirconization treatment (ZrO₂ 50-100 mg/m2), replacing traditional chromates (RoHS compliance).
2. Coating formula:
- Resin matrix: acrylic resin (temperature resistance -30℃~130℃) or epoxy-modified silicone (temperature resistance>150℃).
- Functional additives: nano-SiO₂ (enhanced wear resistance), quaternary ammonium salt (antibacterial), phosphate (improved adhesion).
3. Curing process:
- Hot air curing: 3-5 minutes at 180℃-220℃ to form a cross-linked network structure.
Methods to Test Coating Performance:
- Contact angle test: According to GB/T 30447-2013, use a contact angle meter (such as Krüss DSA100).
- Adhesion test: Cross-hatch method (ISO 2409), rating 0-5 (0 means no peeling).
- Moisture and heat resistance: 500 hours in 85℃ / 85% RH environment, the coating has no blistering or peeling.
Gree’s 2023 technical white paper shows that hydrophilic foil with nano-composite coating can extend the fin life to more than 15 years.
How to Choose Hydrophilic Foil Thickness
The thickness of the hydrophilic foil needs to balance thermal conductivity, strength and cost:
- 0.1mm foil (tolerance ±0.005mm):
- Advantages: lightweight (30% weight reduction), suitable for microchannel heat exchangers (12% reduction in pressure drop on the refrigerant side).
- Applications: household variable frequency air conditioners (such as Midea), commercial VRF systems.
- Restrictions: stamping depth ≤5mm, otherwise it is easy to crack.
- 0.15mm foil (tolerance ±0.008mm):
- Advantages: high rigidity (40% increase in anti-collapse ability), suitable for long fin (>15mm) design.
- Applications: industrial chillers, low-temperature heat pumps (-25℃ environment).
- Restrictions: material cost increases by 20%, and a high-tonnage punch press (>200 tons) is required.
Hydrophilic foil thickness calculation formula: t=PxL2 / 8xσxh
Among them: t = thickness, P = wind pressure, L = fin span, σ = yield strength, h = fin height.
For example, a 5HP air conditioner uses 0.12mm foil (yield strength ≥ 120MPa) at a wind speed of 2m/s, which can take into account both cost and anti-deformation requirements.
How To Evaluate The Corrosion Resistance of Hydrophilic Foils
Corrosion resistance is the core indicator of hydrophilic foil. The evaluation methods include:
1.Neutral Salt Spray Test (NSS):
- Standard: ASTM B117, 5% NaCl solution, continuous spray at 35℃.
- Qualification standard: 8011 alloy + H18 foil must be free of red rust for ≥720 hours.
2.Cyclic Corrosion Test (CCT):
- Standard: SAE J2334, simulated wet heat (50℃/100%RH)-drying-salt spray cycle.
- Qualification standard: Coating adhesion ≥B grade after 20 cycles.
3.Actual Working Condition Simulation:
- Coastal area: Cl⁻ concentration ≥200mg/m³, the coating needs to contain silane coupling agent (to improve density).
- Industrial area: In SO₂ pollution environment, coatings containing molybdate corrosion inhibitors are preferred.
Case: Haier’s air conditioners in the Southeast Asian market use a double-layer coating (bottom layer zirconium + surface layer SiO₂ composite), with a salt spray life of 1,200 hours, 50% higher than that of a single-layer coating.


