What Is An Aluminum Heat Sink?
Aluminum heat sink is one of the most commonly used heat sinks. It is a heat dissipation device used in electronic equipment and other heat-sensitive applications. Its main function is to reduce the temperature of heat sources (such as integrated circuits, processors, LEDs, etc.) by absorbing and conducting heat.
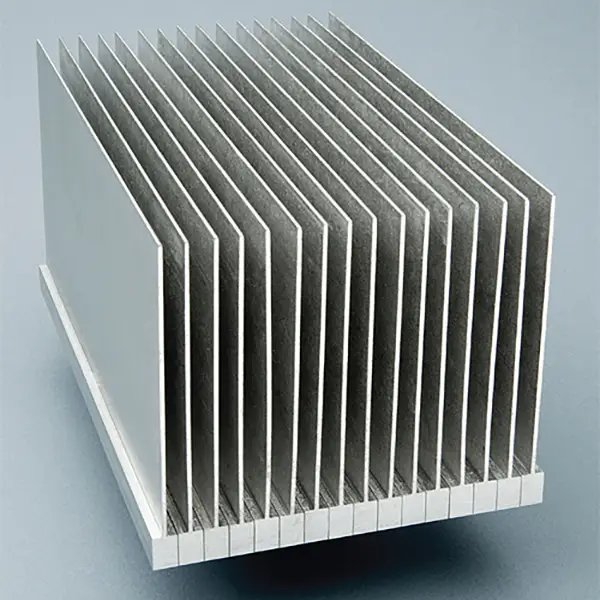

Aluminum heat sinks are widely used because aluminum has many properties suitable for heat dissipation applications. First, aluminum has a higher thermal conductivity. Although its thermal conductivity is about half that of copper, aluminum costs less and is lighter. Compared to copper, aluminum for heat sinks are able to be used in humid or harsh environments. Aluminum is relatively simple to process and manufacture, and can come in a variety of shapes and sizes to meet different cooling needs.
How Does Aluminum Heatsink Work?
The working principle of aluminium radiator is based on the physical principles of heat conduction and natural convection.
Aluminum heat sink uses the high thermal conductivity properties of metallic aluminum to quickly conduct heat from the surface of the electronic device to the surface of the heat sink. Aluminum heat sinks usually have many fins, which are used to increase the surface area for better dissipation of heat. Once the heat is conducted to the surface of the aluminum heat sink, the next process is to further dissipate the heat through natural convection. When the heat on the surface of the radiator exceeds the ambient temperature, the air will be heated and rise, forming a temperature gradient. This temperature difference causes the movement of air, known as natural convection. Through natural convection, hot air is replaced with cooler ambient air, rapidly dissipating heat.
In some cases, aluminium heat sink can also be combined with fans or other cooling devices to increase heat dissipation. These cooling devices can further enhance air flow, provide a larger surface area for heat dissipation, and increase heat dissipation efficiency.
What Are The Advantages Of Aluminum Heat Sink?
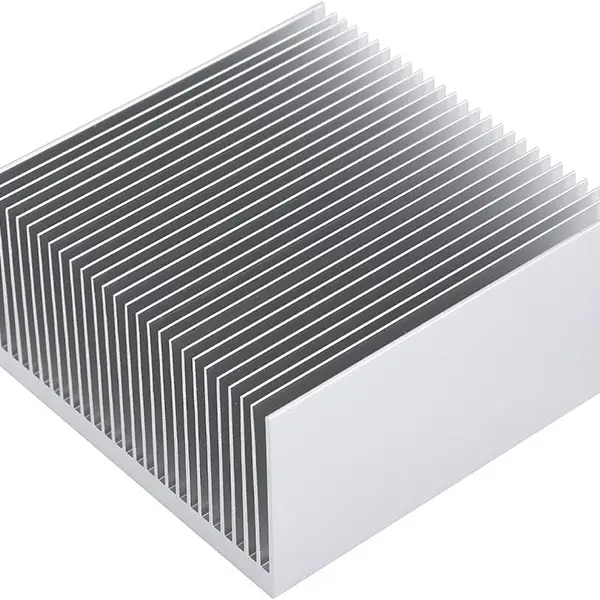
- Lightweight: Due to the lightweight characteristics of aluminum alloy materials, aluminium heat sink are lighter than traditional copper radiators, which can reduce the overall weight of the equipment.
- High heat dissipation efficiency: Aluminum alloy heat sink have excellent heat dissipation performance. Compared with traditional copper radiators, they have higher heat dissipation efficiency and can dissipate heat faster.
- Simple manufacturing process: The manufacturing process of aluminum heat sink is relatively simple, the production cost is low, and large quantities of products can be produced more cheaply.
- Good corrosion resistance: Aluminium alloy heat sink has excellent oxidation resistance and anti-corrosion properties, and are not prone to rust or oxidation problems after long-term use.
What Alloys Are Commonly Used In Aluminum Heat Sink?
Commonly used alloys for aluminum heat sinks include the following:
Aluminum alloy series: 6061 and 6063 aluminum are one of the most commonly used radiator materials. They have good workability, strength and corrosion resistance. 6061 aluminum alloy is usually used for radiators with high strength requirements, while 6063 aluminum alloy is suitable for applications that require better heat dissipation performance and excellent appearance.
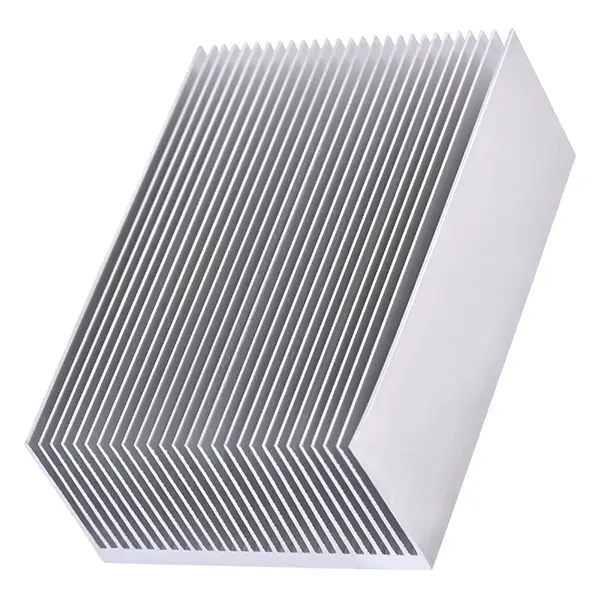

Pure aluminum: Pure aluminum (aluminum 1050, aluminum 1060, etc. in the aluminum alloy series) is often used in heat sinks for lower power applications and price-sensitive products. Pure aluminum has good thermal conductivity and thermal conductivity, but its relative strength is low.
Aluminum alloy: Some other common aluminum alloys include 3003 aluminum, 3004 aluminum and 3005 aluminum. These alloys offer high corrosion resistance and good weldability, making them suitable for many common heat sink applications.
Aluminum silicon alloys: silicon aluminum alloys are commonly used in high-performance heat sinks, especially in the automotive and aerospace fields. Silumin alloy improves the strength and wear resistance of the material by adding silicon element while maintaining good thermal conductivity.
How To Classify Aluminum Radiators?
Based on the method of manufacturing aluminum radiators, we can divide aluminum radiators into these five categories: die-cast aluminum radiators, profile aluminum radiators, composite aluminum radiators, copper-aluminum composite radiators and steel-aluminum composite radiators.
Aluminum Extrusion Heat Sink:
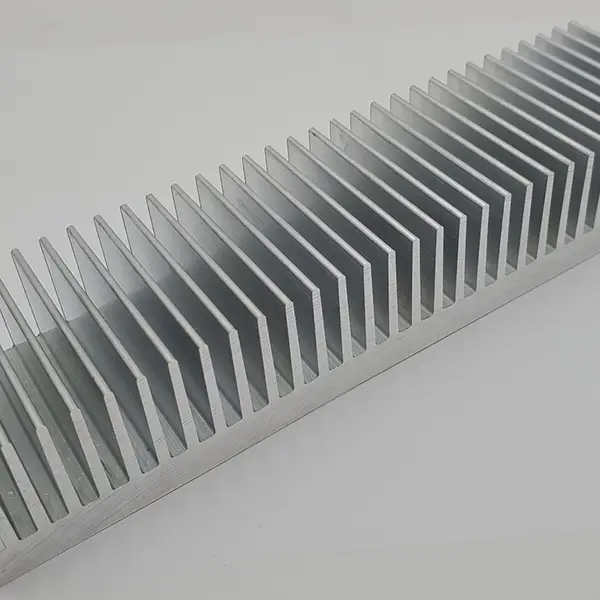
Production raw materials: Adopt die-casting process, using aluminum alloy as the main raw material. Commonly used aluminum alloys include ADC12, A380, etc.
Main uses: Aluminum extrusion heat sinks are commonly used in automobiles, mechanical equipment, electronic products and other fields. They usually have strong durability, high thermal conductivity and good air circulation, and are suitable for various high temperature and high pressure environments.
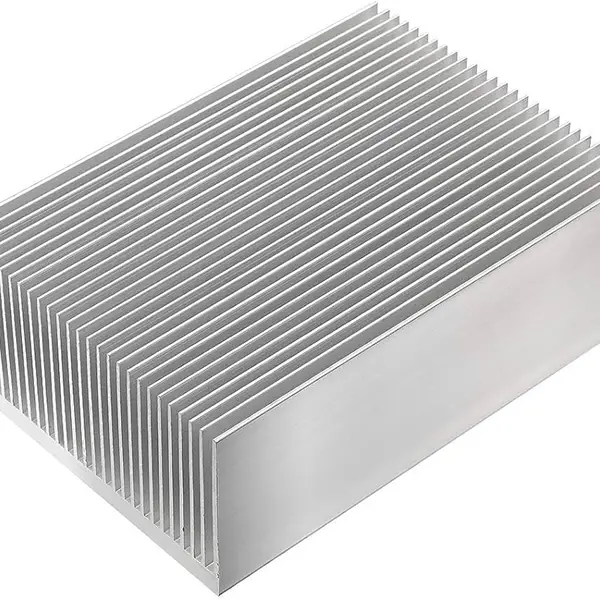
Aluminum Profile Radiator:
Production raw materials: Made of aluminum profiles. Commonly used aluminum alloy profiles include aluminum 6061, aluminum 6063, etc.
Main uses: Radiator aluminum profile is commonly used in electronic equipment, LED lamps, solar products and other fields. They have good heat dissipation performance, large heat dissipation area and light weight, and can be widely used in small spaces or situations where efficient heat dissipation is required.
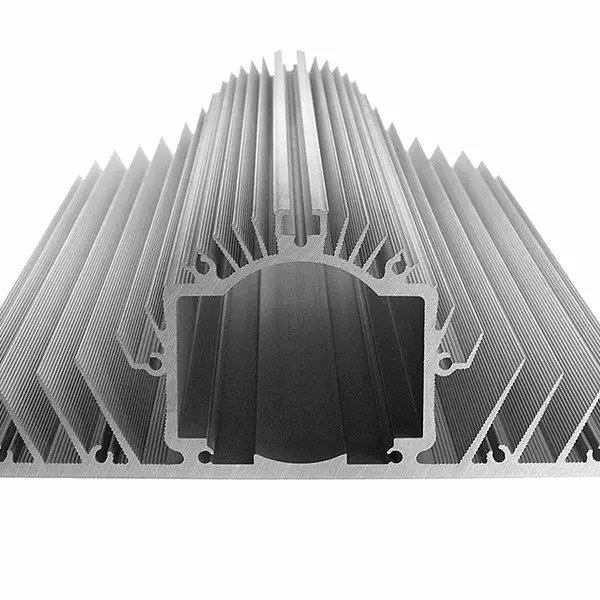
Composite Aluminum Heat Sink:

Production raw materials: Made of aluminum material and other materials, such as copper, aluminum alloy, etc.
Main uses: Composite aluminum radiators are often used in automobile engine cooling systems and power electronic equipment for heat dissipation. Its structural advantage lies in the complementary advantages of aluminum and other materials, such as the combination of superior thermal conductivity and good corrosion resistance.
Copper-Aluminum Composite Heat Sink:
Materials: Made of copper and aluminum.
Main uses: Copper-aluminum composite heat sinks are often used in high-end electronic equipment, solar energy and other fields. Copper has good thermal conductivity, while aluminum has a lower density and good processability. Copper-aluminum composite heat sinks combine the advantages of both materials and have excellent heat conduction efficiency and corrosion resistance.

Steel Aluminum Composite Radiator:

Production materials: Composite of two materials: steel and aluminum.
Main uses: Steel-aluminum composite radiators are mainly used in automobiles, machinery and equipment and other fields. The steel-aluminum composite radiator combines the advantages of steel and aluminum materials, has good strength and durability, and has high heat dissipation performance.
Copper Vs Aluminum Heatsink: Which Is Better?
| Material | Thermal Conductivity(W/m.K) | Specific Heat Capacity(KJ/kg.K) | Density(g/cm3) |
| Cu | 401 | 386 | 8.9 |
| Al | 237 | 900 | 2.7 |
It can be seen from the table parameters that the thermal conductivity coefficient of copper is about 1.69 times that of aluminum. Therefore, when copper and aluminum are used to make a radiator with the same cross-sectional area, pure copper can take away more heat per unit time than pure aluminum. “Copper is more efficient than pure aluminum.” Aluminum absorbs heat quickly.” The specific heat capacity of copper is smaller than that of aluminum. If copper lowers its temperature by 1 degree, it should dissipate less heat than aluminum. So, does copper really dissipate heat faster than aluminum?
No, the density of copper is 8.9kg/m3, while that of aluminum is only 2.7kg/m3, which is close to 3.3 times that of aluminum. Therefore, when making a heat sink of the same volume, copper will be nearly 3.3 times larger than aluminum in terms of mass. Pure copper The heat capacity of the material is still nearly half greater than that of pure aluminum. As the heat capacity increases, heat dissipation becomes slower. Through the explanation of the above theory, “copper does not dissipate heat as quickly as aluminum.” This theory can be used when choosing a radiator. If you choose a pure copper radiator, you should choose a fan product with a higher speed and larger air volume to avoid the copper heat being unable to dissipate and creating a heat dissipation bottleneck.
The heat dissipation part is more complicated. I personally think that the advantages of aluminum are in the following aspects:
1. Cheap, low density, easy to process, the hardness of aluminum alloy is much better than that of pure copper, and it provides the largest heat dissipation area within the range that the motherboard/fastener can bear (the heat dissipation area should be 100% for the heat dissipation speed) greatest impact)
2. The same volume of copper absorbs the same heat and the temperature rises slowly. This also makes the temperature difference between copper and the surrounding environment low, which is not conducive to the fastest heat release. Copper conducts heat quickly, has high cost, and has high heat enthalpy. Simply put, copper itself transfers heat quickly, but the speed at which it is transferred to another substance is questioned.


